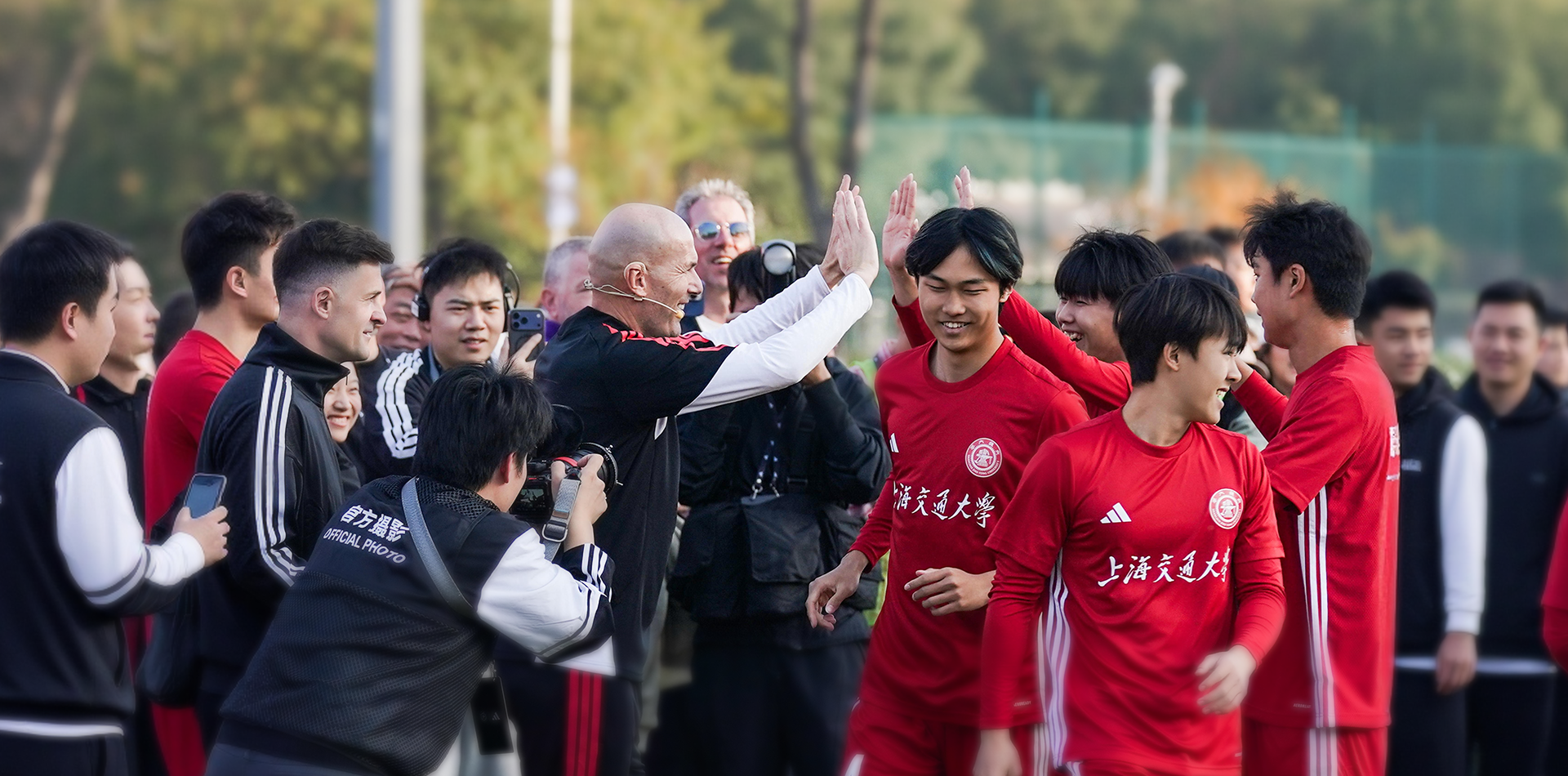
At the heart of Shanghai, SJTU is more than a university—with its academic prestige, cutting-edge research, culture of innovation, and vibrant campus life, it serves as a launchpad for global minds.
Why SJTU?




Study@SJTU
Founded in 1896, Shanghai Jiao Tong University is one of China’s top universities, recognized internationally for its excellence in education, research, and global impact.
Work@SJTU
SJTU advances its “Talent-Empowered University Development” strategy, pioneering tenure-track systems and categorized career pathways with multi-dimensional evaluations. Guided by a philosophy of attracting, retaining, and empowering talents through trust, mentorship, and holistic care, we have established a unique faculty development model centered on talent pyramids and academic honors frameworks, forming a distinctive talent cultivation ecosystem.
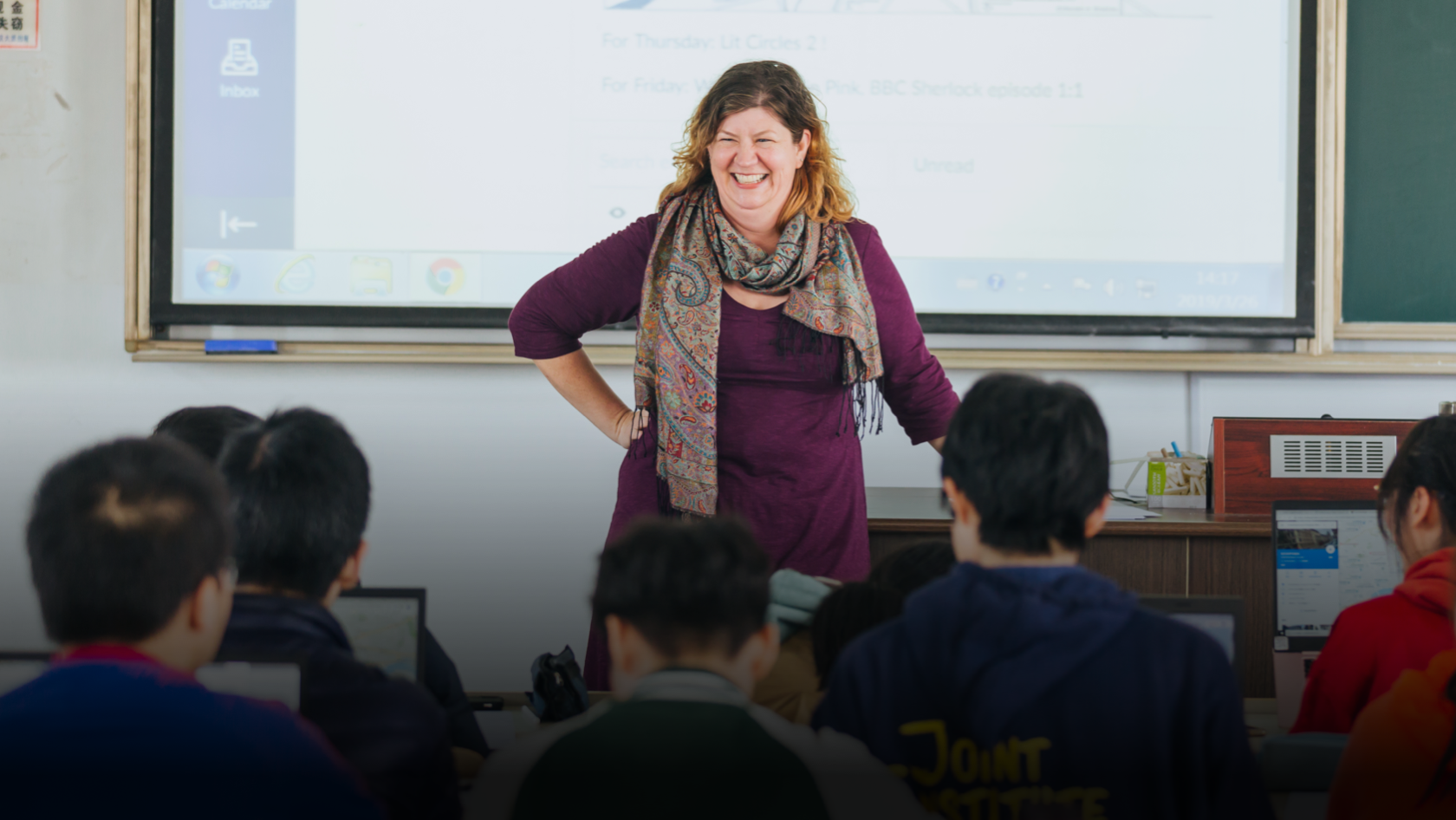

Join Us
SJTU in the News
Noticeboard
Upcoming Events
Global Network
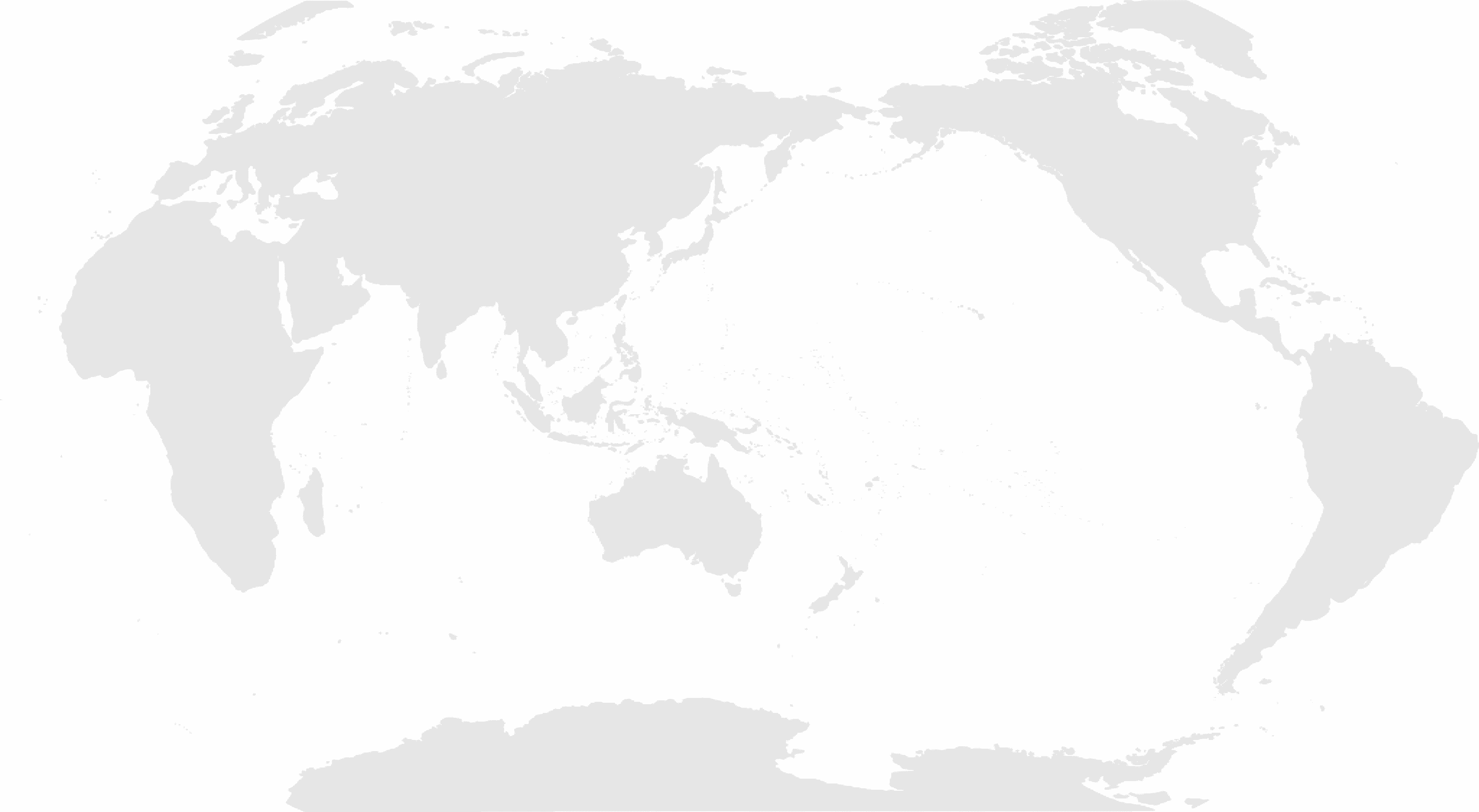






- 80+ partners
- 20 exchange programs
- 380+ international students
- 45+ foreign teachers
- 5+ partners
- 130+ international students
- 1+ foreign teachers
- 140+ partners
- 60 exchange programs
- 900+ international students
- 20+ foreign teachers
- 5+ partners
- 100+ international students
- 1+ foreign teachers
- 70+ partners
- 60 exchange programs
- 2200+ international students
- 45+ foreign teachers
- 10+ partners
- 10 exchange programs
- 80+ international students
- 4+ foreign teachers

In the 1980s, the German Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU) was established to support German language instruction within the university and its exchanges with Germany. Today, as part of SJTU’s “Global SJTU” initiative, the Center has redefined its mission around four core functions: facilitating connections and exchanges, promoting collaborative innovation, integrating with university initiatives, and serving as a regional hub for outreach. These pillars aim to further strengthen SJTU’s partnership with German institutions.
In 2023, the German Center officially launched its Munich branch, featuring teaching and logistical support facilities. The Center is actively expanding its mobile classroom initiative in Germany, while also serving as the secretariat of the Ministry of Education’s Sino-German Innovation Consortium for Industry, Academia, and Applied Research. In doing so, it is helping develop a more structured and impactful platform for China-Germany cooperation.

SJTU Asia-Pacific Graduate Institute (SJTU-APGI) is an extension of SJTU’s education and research efforts, as well as a platform for overseas resource integration and internationalization.
The overall goal of SJTU-APGI is to promote the innovation of systems and integration of resources, and in turn, open up new global prospects in the fields of education and research.