Project Summary Report
[Global Engagement Program] Camp on Risk Assessment of Drinking Water and the Control Strategies in Pakistan
At present, more than a billion people in the world lack access to safe drinking water, especially in some developing countries. Pakistan is one of those countries with severe drinking water pollution. Because of serious environmental pollution and imperfect health system, residents are facing great risks from drinking water. Islamabad is the capital city of Pakistan, neighboring to Rawalpindi, and the quality of drinking water in these cities require major attention.
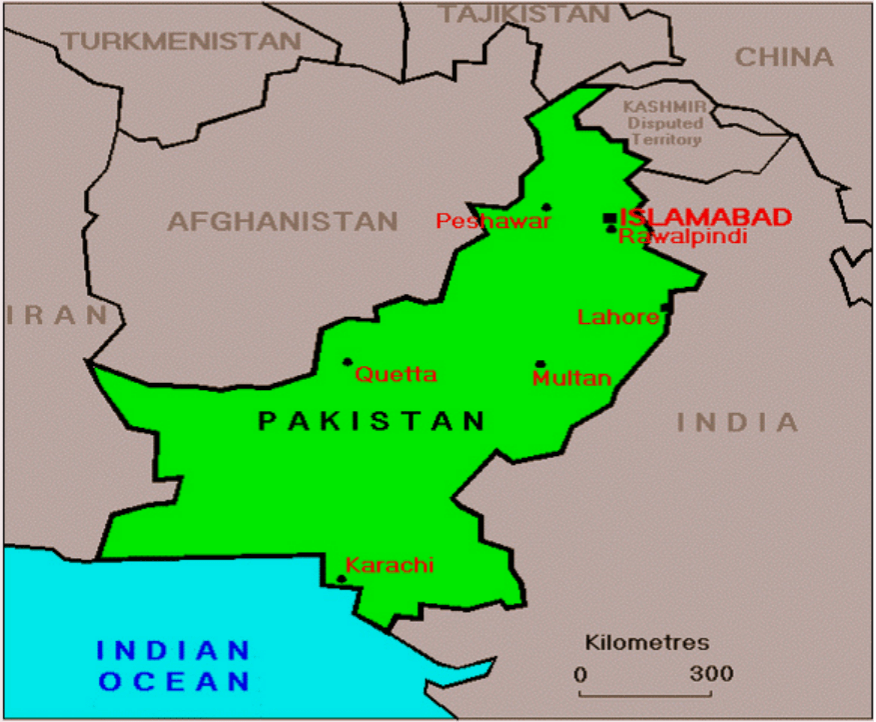
The map of Pakistan highlighting the twin cities of Islamabad and Rawalpindi
This event is part of a series of initiatives under the framework of Global Engagement Program 2018 of Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Professional team members from the School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology of SJTU and the Department of Biosciences of COMSATS University Islamabad utilized the available technology and talent, and took the current drinking water quality problem in the twin cities of Pakistan as their challenge work. The team work included on-site field investigations, international team cooperation, and professional guidance to the water utilities. This allowed the international students to participate and complete the challenging scientific and technological activities.

A team of researchers, led by Professor Xiaohui Bai, started off from Shanghai on 23rd July to work on the project of “The Microbial Risk Assessment and Control Strategy for Drinking Water Quality in Pakistan”. The team consisted of Hira Khan (PhD student), Wang Yang (Masters student) and Liu Ming Kun (Masters student) from the School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, SJTU. They reached Islamabad on the morning of 24th July 2018 and later in the afternoon they went to COMSATS University Islamabad (CUI). Dr. Arshad Rafiq (Head of Biosciences Department of CUI), Dr. Maleeha Azam and Dr. Liaqat Ali welcomed the team and discussed about the work arrangements and project plan for the coming days.
Sample Collection
From the very next day, the team started to visit the different water treatment plants one by one. Basically there are three different waterworks operating in order to supply the drinking water to the twin cities of Pakistan. There is Rawal Filtration Plant, supplying drinking water to Rawalpindi city, Simly water treatment plant supplying water to Islamabad city and Sangjani water treatment plant which supplies water to both cities. Along with these surface water sources, both cities also use ground water for drinking purposes.
Distribution of water filtration plants in Islamabad
The team set the sampling locations as follows. Each day the team went to one of the locations, sites were inspected carefully, the water treatment process was being introduced by the water utilities, physical parameters were measured on the spot, and samples were brought back to the laboratory for microbial counts analysis and microbial safety assessment.
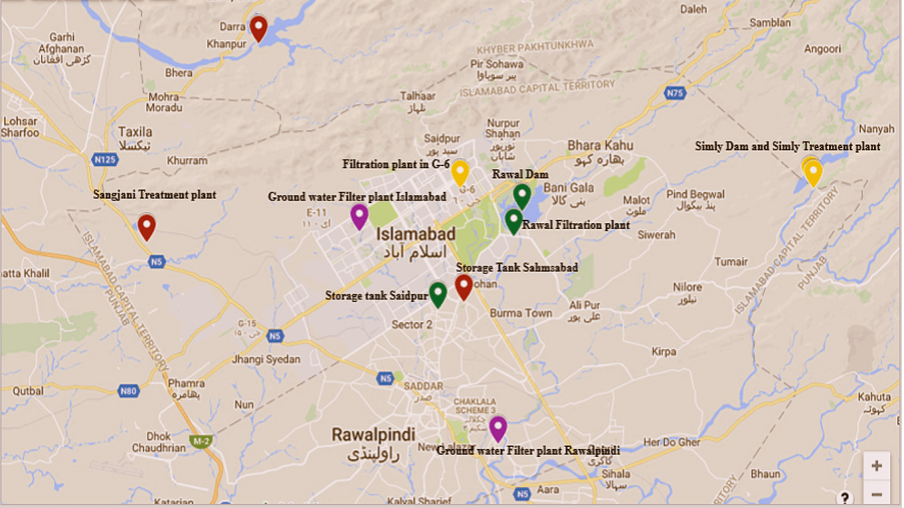
Sampling points for the collection of samples (Different colors on the locations show different sources of water)
Simly Water Filtration Plant
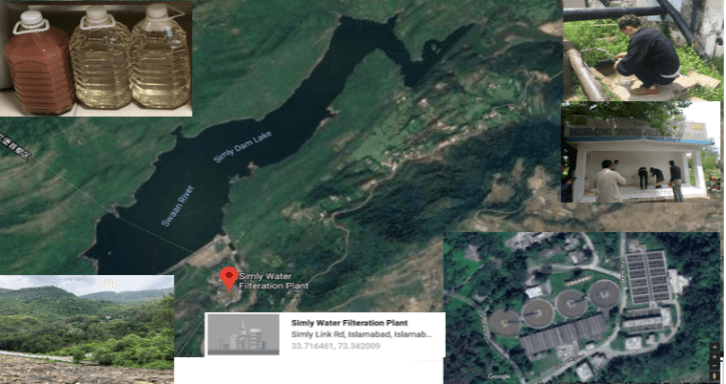
The main problem we observed in simly water plant was that the total chlorine concentration in the effluent was particularly high, reaching upto 8.6mg/l which could cause high amount of disinfection byproducts like THMs, HAAs, NDMA. It was said that, because the water distribution system is too long (pipeline system from the water filtration plant to the end of consumers), so this much chlorine is added into the effluent to remove microbes on the way. However, this much amount of chlorine is not good for the health of human beings taking this water to drink because of the high disinfection by-products and pungent odors left in the water.
Rawal Lake Filtration Plant
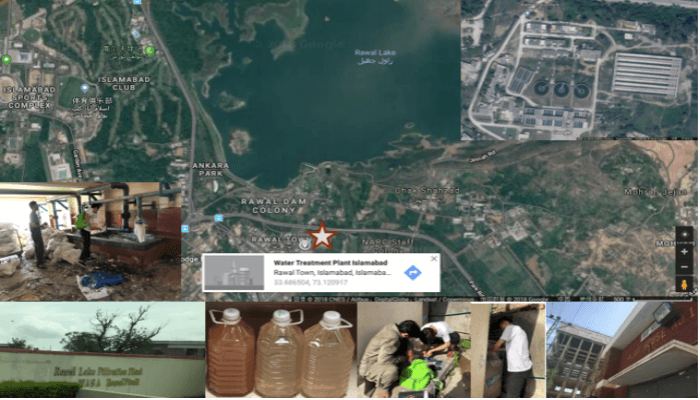
The main problem with WASA Water Plant was its management, each treatment equipment could not effectively play the corresponding role. We went there two times, once during a rainy day and once without rain. On the rainy day the water turbidity in the effluent was found up to 38NTU, which is far more than the local standard of Pakistan (5NTU). Water was very dirty and the most serious concern was that we were able to detect fecal contamination indicator bacteria of E. coli in the collected samples. So we suggested to increase the total chlorine level in the effluent to 2 mg/L above to guarantee the microbial safety of the treated water. When we went to this plant second time, they increase the total chlorine concentration to 2.2mg/L and the total coliform could not be found in our measurement.
Sangjani Water Filtration Plant
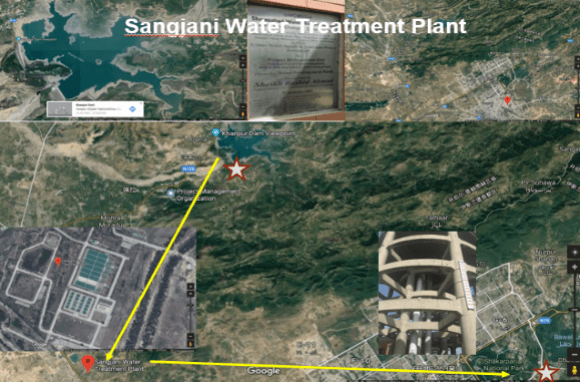
Sangjani Water Treatment Plant was found to be the most effective in all the waterworks we visited. The main reason was because its raw water was from the Khanpur Dam, the raw water quality was good and the treated water basically met the local standards. But it was found that even the effluent water met the standards, the total chlorine concentration in the effluent is still too low and during the process of water supply, there was still some problems. As after the treated water pass through the tower, HPC significantly increased to 10000cfu/ml, and the presence of Escherichia coli was detected, which indicates that the water supply process is still contaminated.
Worryingly, we stayed at the Embassy Hotel water, whose water quality was also found very poor, HPC>10000cfu/ml, and even E. coli were detected there, which was the main reason our team, during our stay there was gone through varying degrees of diarrhea.
Ground water and multi-filtration plant
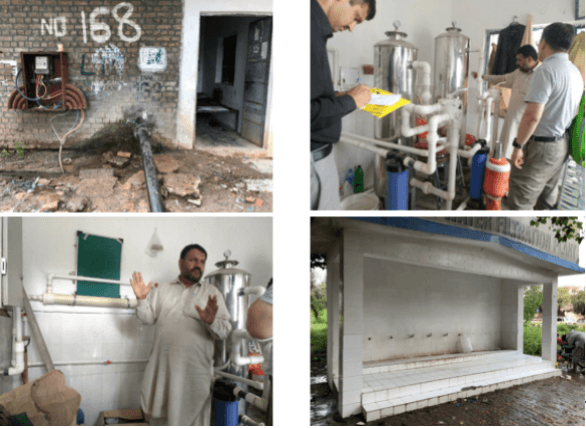

We sampled some ground water samples as well, there are small filtration plants installed throughout the cities to take water from source water/ ground water and filter them for consuming purposes. Ground water quality was found better as compared to source water in the twin cities. It was much cleaner to drink. That is why we also found that majority of local residents use ground water as source of their drinking water. Some people have personal tubewells installed in their houses from which they can dug up the water and use it for daily life purposes. For drinking purposes, there are small filtration plants installed throughout the city which filter ground water and people can take it freely from the filtration plants.
Methodology:
The research team inspected each of the sampling sites carefully and the water treatment process was understood under the guidance of the water authorities in the treatment plants. Physical parameters were measured on the spot and samples were collected to check for the heterotrophic plate count (HPC) and Total coliform detection.

Laboratory work performed at CUI, Biosciences department for the analysis of collected samples

Physical parametric analysis of the samples on the site (Left), Site inspection of Rawal Dam (Right)
We took water samples from all the explained sampling points and did the following procedures during our stay in Pakistan.
1. Water samples were filtered to get enough bacteria captured on filter membranes to be brought back to Shanghai
2. Heterotrophic Plate Count was detected from each of the collected samples
3. Total coliform bacteria were detected from all the collected samples
When we reach back to Shanghai
1. DNA was extracted from the collected samples
2. Anntibiotic Resistant genes (MCR-1 and NDM-1) were detected from the samples
3. DNA was sent for 16S rRNA high throughput sequencing to know the exact bacterial community structure of the collected samples.
Results

Water samples collected from different sources
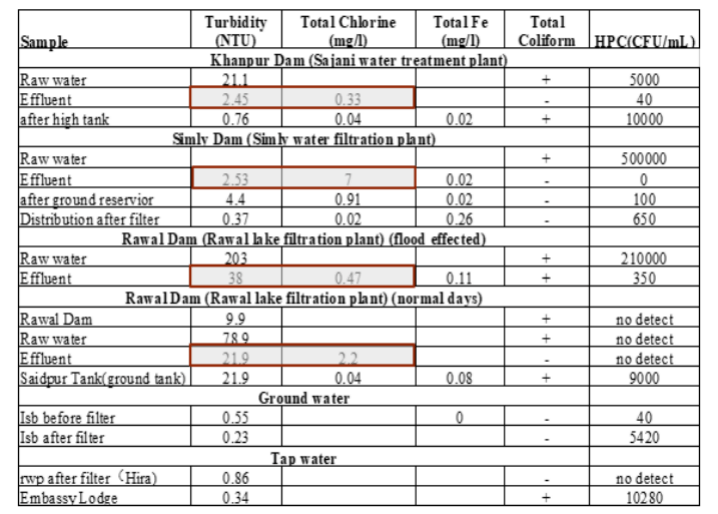
Water Quality in different plants
The results we got so far are shown in the table below. As it is discussed previously that the comparison of ground water and source water showed that the ground water quality is better as compared to source water.
If we compare all the source water samples, so we found out that the sangjani water treatment plant was much better than the WASA and the Simly water treatment plant.
But the presence of coliform bacteria in water supply system is a major problem.
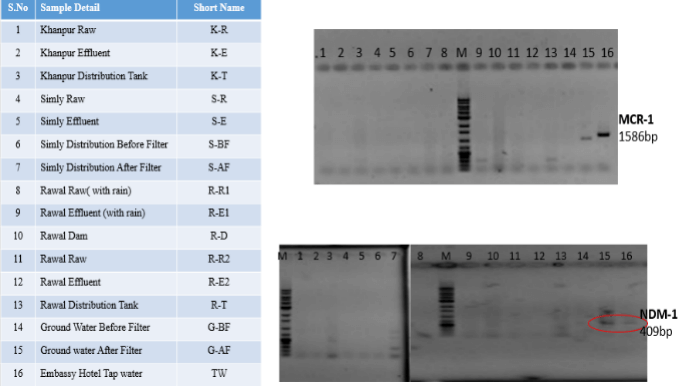
Antibiotic resistant gene detection (MCR-1 and NDM-1)
We also detected the presence of ARGs (MCR-1 and NDM-1) in the water samples after distribution system, so that is also very alarming.
These two ARGs provide resistance to last resort antibiotics, so their presence in the distribution system could have a poor effect on the human health.
Some potential Risks in drinking water in Islamabad
During the inspection the team discovered that the water treatment plants had the capacity to deliver a large amount of water to the residents, but due to poor maintenance, lack of professional management and the shortage of government funds, the quality of drinking water is not maintained as it should be. Groundwater was found to be better in quality as compared to surface water based on the initial analysis.
The surface water treatment plants can’t supply good and safe drinking water to Islamabad people, the plants don’t work well;
Because of the poor performance of the Rawal lake filtration plant, the effluent turbidity is 38NTU (5NTU for PK Standard), total chlorine is 0.47mg/L (0.5-1.5mg/L for PK Standard), Total Coliform and large number of heterotrophic bacteria were found in treated water; Maybe more waterborne pathogens can be found after 16S rDNA high throughput sequencing. Maybe the same thing will be found in Khanpur dam plant (Sangjani water filtration plant).
For the Simly water filtration plant, total Coliform and heterotrophic bacteria were not found, but it was because of the high chlorine concentration of 7mg/L. As the Simly dam receives water from upstream river containing different organics, the treated water after conventional physiochemical water treatment process must have some disinfectant byproducts formed, such as THMs, HAAs, NDMA etc. All these harmful chemicals may cause some mutation of human cells and results in some cancer diseases.
All these hypothesizes need more detail measurements for disinfectant byproducts and bacteria diversity.
Control Strategies for Safe drinking water in Islamabad
1. New activities from new Prime Minister to improve the economy in PK;
2. Redesign the position and depth of the intakes for Rawal lake filtration plant and Simly dam filtration plant;
3. Optimize the dosage of coagulant and the flocculation process to improve the sedimentation and make the water clear in all surface water plants;
4. To investigate the residual chlorine decay in water distribution system and find the safe chlorine dosage for the treated water of all surface water plants.

Meeting with the Rector of COMSATS, Islamabad
During the visit, the team was also invited to meet the Rector of CUI, Prof. Dr. Raheel Qamar (T.I), who showed a great supportive gesture to facilitate this program smoothly and effectively. The team is really hopeful to get some interesting results from the samples. After careful analysis and detailed investigation, the team will try its best to introduce valuable and effective strategies to make the quality of water better and healthier for consuming purposes. This project will help to strengthen the traditional friendship between China and Pakistan.

Special Thanks to:
International Affairs Division of SJTU for providing funds and CUI for providing the facilities and working environment in Islamabad